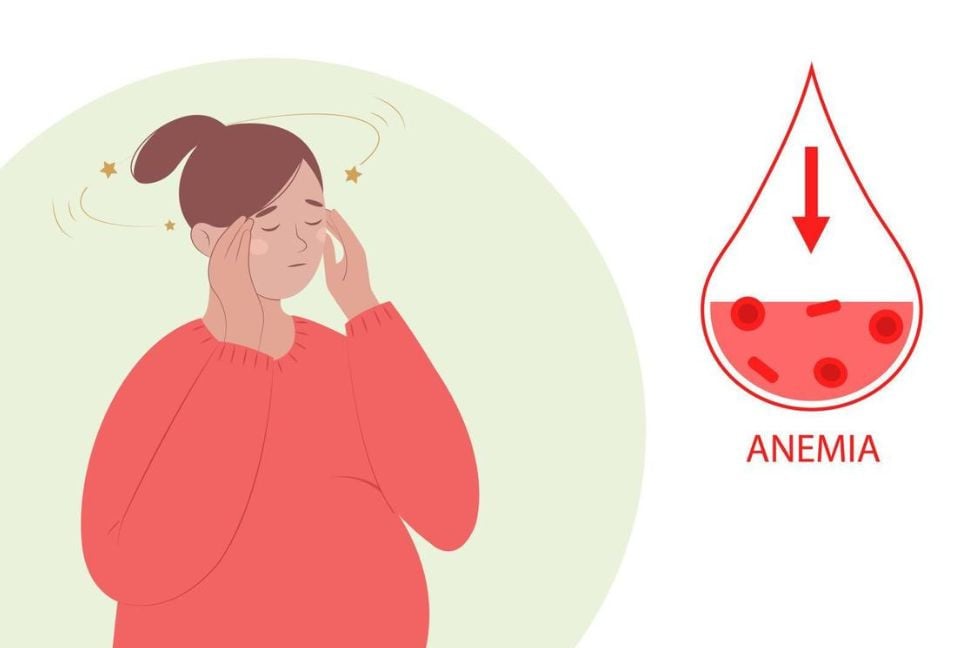
Feeling dizzy might not just be a sign of stress—it could indicate anaemia. Anaemia occurs when haemoglobin levels are low or the number of red blood cells decreases, leading to insufficient oxygen supply to the body's tissues. This condition is often detected through routine blood tests.
Common causes of anaemia
Dr. Sneha S, a consultant in internal medicine at Manipal Hospital in India, explains that the most common cause of anaemia is iron deficiency. This often results from poor diet, chronic blood loss (like heavy menstrual bleeding or gastrointestinal ulcers), or conditions that impair nutrient absorption.
Deficiencies in vitamin B12 and folic acid can also lead to anaemia, typically due to inadequate intake, malabsorption disorders (such as pernicious anaemia and celiac disease), or increased needs during pregnancy.
In some cases, anaemia can stem from the premature breakdown of red blood cells, known as hemolysis. This may occur due to genetic conditions like thalassemia, hereditary spherocytosis, and sickle cell anaemia, or autoimmune disorders.
Aplastic anaemia, a rare but serious form, happens when the bone marrow fails to produce enough red blood cells, often triggered by autoimmune diseases, infections, or toxic chemical exposure.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Typical symptoms of anaemia include fatigue, dizziness, heart palpitations, shortness of breath, loss of appetite, and excessive hair fall—especially in women. Some specific types of anaemia show unique symptoms:
Iron deficiency anaemia: Craving non-food items (pica) and spoon-shaped nails.
Vitamin B12 deficiency anaemia: Neurological issues such as tingling and numbness.
Hemolytic anaemia: Jaundice.
Diagnosing anaemia typically involves tests like a Complete Blood Count (CBC), Peripheral Blood Smear, Serum Iron Studies, and Vitamin B12 and Folate Level assessments. Additional tests may be needed to pinpoint the exact cause.
Treatment options
Treatment varies based on the underlying issue. Iron deficiency anaemia is treated with iron supplements, while vitamin B12 deficiency requires high-dose oral or intramuscular supplements. In severe cases, blood transfusions or more advanced medical interventions might be necessary.
If you’re experiencing unexplained dizziness or fatigue, consulting a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment is essential.
Bd-pratidin English/FNC