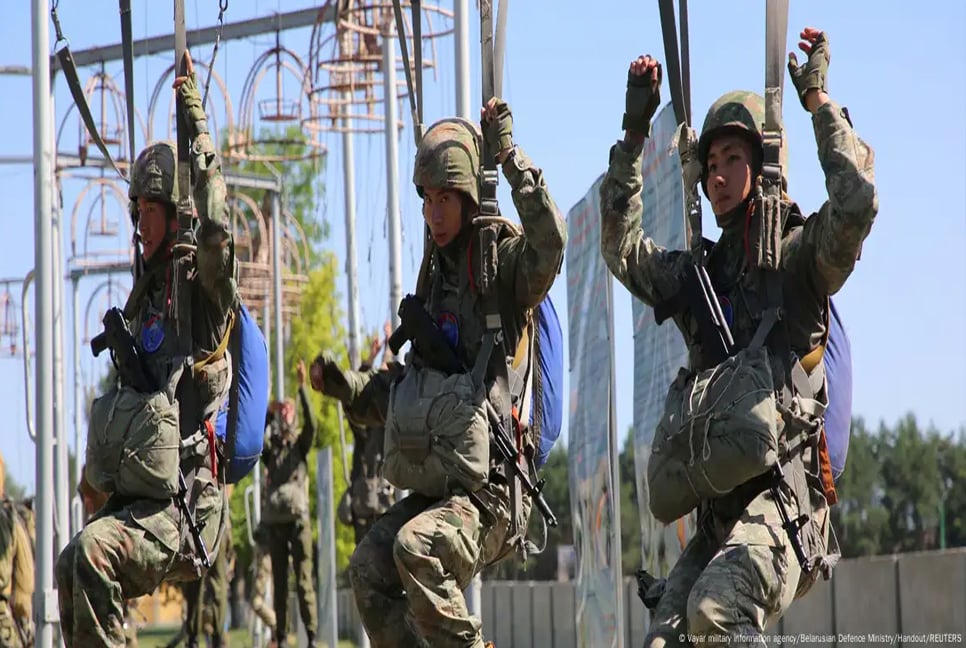
On Monday, Belarus and China began a joint anti-terrorism military drill. Dubbed Eagle Assault 2024, the 11-day exercise will see troops practice night landings, overcome water obstacles and undetake urban combat drills.
The joint exercise follows Belarus joining the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), a Eurasian political, economic and defense organization led by Russia and China, earlier this month.
The experts in the region were asked why Belarus needs the SCO and what the joint drills with China could mean for the region, reports DW.
Fighting terrorism?
Belarus has become the 10th member of the SCO, which originally consisted of the founders China and Russia, as well as Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. Since the organization's founding, Indian, Pakistan and Iran have also joined it.
At first, the SCO was intended to address border disputes between the first five members. Later, joint security issues began to take center stage. Member states regularly take part in joint anti-terrorism exercises.
Most experts agree that members don't get any sort of financial or economic support from the SCO. Instead, its become more of a platform for negotiations and talks.
"Various heads of state and government come together in the SCO," said Pavel Matsukevich, a researcher at the think tank Center for New Ideas, which specializes in Belarusian politics. "They can pursue bilateral talks at the sidelines of SCO summit meetings."
Russian dependency
Belarus had ties with China and India even before joining the SCO. For years, the country's second-largest trading partner after Russia was the European Union (EU).
However, Anastasia Luzgina, a researcher at the Belarusian Economic Research and Outreach Center, or BEROC, believes that Belarus' authoritarian President Alexander Lukashenko has since made his country an international pariah. And "the economy has had to adapt to this new reality," she said.
Sanctions against Belarus — in part a response to fraudulent elections in 2020 and the state's human rights abuses against those protesting their outcome — have caused the nation's economy to shrink, the expert explained.
"At first, state officials turned toward Russia but now they are looking for other markets," Luzgina said. As Belarus found it too risky to rely entirely on Russia', Minsk was searching for alternative partners should Russia fall into a recession, she added.
The researcher also pointed out that Belarus was seeking to replace its European market with Asian partners, especially in China. She believes Belarus' new membership in the SCO is in line with this strategy.
A 'marriage of convenience'
Being an SCO member could also increase Belarus‘ chances of joining BRICS, Matsukevich believes. Currently comprising Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, the United Arab Emirates, Iran, Egypt and Ethiopia, the BRICS group wants to be seen as a challenger to the West's G7 bloc.
"To Belarus, this is a marriage of convenience," Matsukevich, a former diplomat, said. "The EU market is closed to them and access to ports is also closed to them. The country must resort to using Russian and Chinese infrastructure, and pursuing trade with the third world."
He added that, in joining the SCO and cozying up to BRICS, Minsk also wants to decrease its dependence on Russia. And Lukashenko apparently believes that he will get something in return if he supports Russia, China or India, Matsukevich argued.
Experts say China is Belarus' second-most important trading partner after Russia. "About 70% of Belarusian trade is with to Russia, and about 10% goes to China," Luzgina said.
Belarusian Preisdent Alexander Lukashenko is pursuing closer ties with China, presumably also to move away from his nation's reliance on RussiaImage: Pang Xinglei/Xinhua/IMAGO Images
In that relationship, China dominates, she added. Owing to shrinking trade ties with the EU, Belarus has relied on Chinese machinery, cars and consumer goods while Belarus exports potassium fertilizer — formerly this was sent mostly to Western countries — and food products to China.
Exercises on the Polish border
It may appear that this week's Chinese-Belarusian joint military exercise are a result of Belarus joining the SCO. But in fact they are not the first military drill the two nations have undertaken together. These took place in 2018, in China's northeastern Jinan.
Now the countries are working together in Belarus' southwestern Brest, just 2.8 kilometers (1.7 miles) from the Polish border and 28 kilometers from Ukraine.
However Matsukevich said that Belarus' new SCO membership likely doesn't have much to to do with this military exercise. "Preparing for that takes time. It doesn't happen overnight," he explained. And these kinds of drills always lead to tensions with neighboring countries, he added.
Previously, from 2016 to 2020, before popular protests began in Belarus, Minsk had maintained a dialogue with NATO and even invited observers to its maneuvers. The current exercises in Belarus are more likely to cause a stir in Russia, the expert believes, because the Chinese military is involved and this is all happening within Moscow's sphere of influence.
"I would assess this as a kind of challenge to Russian influence in this area, even though that's not how China is playing it," Matsukevich ocncluded. "These exercises are more evidence of how intensively Belarusian-Chinese relations have developed in all areas."
Bd pratidin English/Lutful Hoque