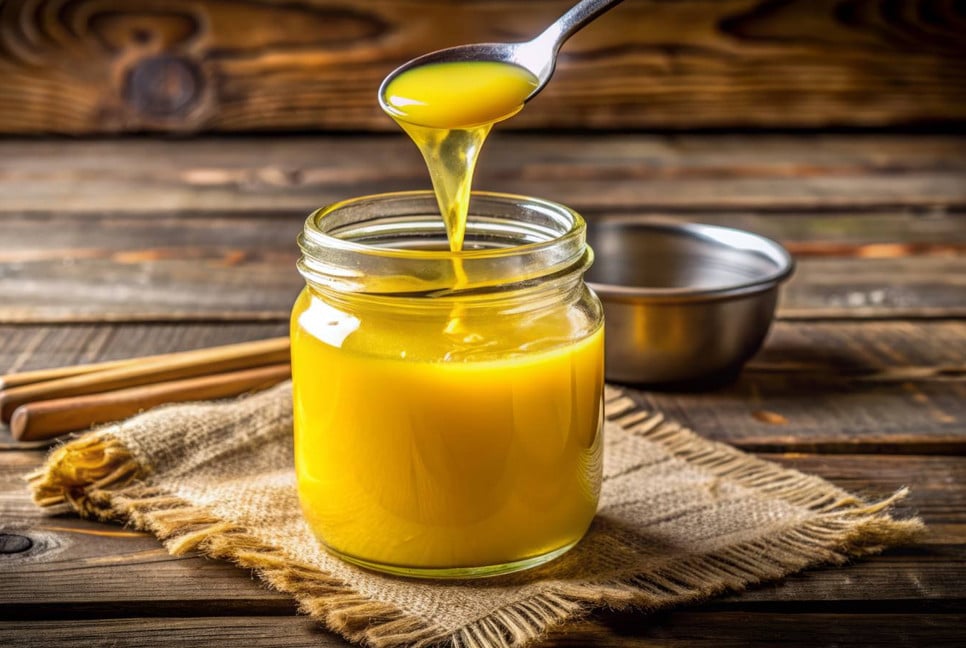
Ghee has long been a cherished staple in kitchens, passed down through generations for its rich flavor and cultural importance. Whether used in your morning paratha or a festive dish, ghee holds a special place in every household. Surprisingly, ghee also offers benefits for managing diabetes. Although ghee is high in fats and calories, it has a low glycemic index and contains healthy fats and antioxidants, which can help regulate blood sugar levels when consumed in moderation.
Diabetes is a chronic condition where the body either doesn't produce enough insulin or cannot use it properly, causing high blood sugar levels. Insulin helps regulate blood sugar, and when it's not functioning correctly, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, potentially damaging organs like the heart, brain, and legs. The number of people with diabetes has risen from 200 million in 1990 to 830 million in 2022, making it a leading cause of death. Understanding diabetes is crucial to prevent serious health complications.
Ghee for diabetes: What are the benefits?
Ghee, also known as clarified butter, is a staple in many traditional diets. Unlike regular butter, ghee is free from lactose and casein, making it easier to digest. Here are 7 key benefits of using ghee for diabetes management:
1. Low glycemic index
Ghee has a low glycemic index (GI), meaning it does not cause a sharp spike in blood sugar levels after consumption. This makes it a safer fat choice for diabetics compared to many other oils and fats, which can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
2. Healthy fats
Ghee is rich in healthy monounsaturated and saturated fats, which are beneficial for heart health. Research published in the IP Journal of Nutrition, Metabolism and Health Science suggests that replacing unhealthy fats with healthy fats like those in ghee can help improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels in type 2 diabetes patients. Eating ghee for diabetes is good because these fats are easily metabolized by the body, unlike processed fats which can cause spikes in blood sugar.
3. Packed with vitamins and antioxidants
Ghee is an excellent source of fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamins A, D, E, and K. These vitamins are essential for maintaining overall health, improving immunity, and supporting eye health. Additionally, it contains antioxidants that help reduce inflammation and protect against oxidative stress. This makes eating ghee for diabetes beneficial.
4. Zero carbohydrates
Since ghee contains no carbohydrates, it won’t impact blood sugar levels. For people with diabetes who need to manage their carbohydrate intake, ghee provides a rich source of energy without raising glucose levels.
5. Linolenic acid
Ghee is a source of linolenic acid, an omega-3 fatty acid, as per the Journal of Food Composition and Analysis. It supports heart health by reducing inflammation and helping to regulate cholesterol levels. This is particularly beneficial for people with diabetes, who are at higher risk of cardiovascular diseases. Ghee for diabetes helps balance overall lipid profiles and supports better heart health.
6. Butyric acid
Apart from linolenic acid, ghee also contains butyric acid, a short-chain fatty acid that promotes gut health, reveals a study published in the Journal of Food Composition and Analysis. It has anti-inflammatory properties and helps improve the digestive process. A healthy gut is crucial for better nutrient absorption and blood sugar control. This is what makes consuming ghee for diabetes a valuable addition to your diet.
7. Promotes digestion
Ghee stimulates the secretion of stomach acids, which helps in better digestion and absorption of nutrients. Research published in the Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine supports this, noting that ghee has been used in Ayurvedic medicine to promote gastrointestinal health, which helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Ghee for diabetes: Are there any side effects?
Ghee can be a great addition to a diabetes-friendly diet, but it is important to use it in moderation. While it has health benefits, eating too much ghee can lead to weight gain because it is high in calories. This could make it harder to control blood sugar levels. Ghee also contains saturated fats, and too much of these fats can raise bad cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart problems—a concern for people with diabetes. To avoid any negative effects, it is best to balance ghee with other healthy fats, like those found in nuts, seeds, and fish. As always, it is a good idea to talk to a doctor or dietitian before making changes to your diabetes-friendly diet.
Ghee for diabetes: How to consume it?
To consume ghee for diabetes, it is important to do so in moderation. A recommended serving is about 1 to 2 teaspoons per day. You can add it to your meals by drizzling it over dal, rice vegetables, curries, or whole grains like quinoa or brown rice. It can also be used for sautéing or cooking at low to medium heat. For breakfast, try adding ghee to oatmeal or whole wheat toast. Avoid excessive use, as ghee is calorie-dense. Pair it with a balanced diet rich in fibre, lean proteins, and healthy fats to help manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Source: healthshots.com
Bd-pratidin English/ Afia