Eating low-carbon foods helps reduce emissions, but some foods actually suck up carbon from the atmosphere, leaving the climate in a better place.
It's possible to make your entire diet carbon-negative, although in today's world, it would require substantial changes to how most people eat, reports BBC.
Overall, food production contributes a quarter of human-caused greenhouse gas emissions.
However, there are some foods that remove more greenhouse gases than they emit, often referred to as "carbon-negative" foods. Producing and eating more of these could help reduce the carbon impact of our food and, in some cases, restore ecosystems in the process.
When plants grow, they take carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air, but when we (or animals) metabolise these plants, this CO2 usually gets released straight back into the air.
We need to permanently remove carbon from the atmosphere, storing it deep in the sea, rocks, soil or trees. There are a few food products and production practices that do this.
Kelp
As kelp and other macroalgae grow, they take in CO2. Parts of the kelp break off and move down to the deep ocean floor where some of that carbon gets stored. These removals are relatively small per kg of kelp, so for kelp-based foods to be carbon-negative, the supply chain has to be very carbon efficient, with minimal transport, packaging and processing.
Locally-sourced kelp therefore has the potential to be carbon-negative (although this represents the minority of cases today). However, buying kelp may provide an incentive to restore the vast areas of kelp forests that have been destroyed; an environmental benefit that goes beyond mitigating climate change.
Bacterial products
Methane-oxidising bacteria are a group of bacteria found in several different environments which consume methane to get energy. This is very useful because methane is a potent greenhouse gas, with each kg causing 30 times more warming than CO2 over a 100-year timescale.
If we eat these bacteria, we metabolise them, releasing CO2. Therefore, eating products containing these bacteria would convert a potent greenhouse gas (methane) into a far less potent one (CO2). Products from these bacteria – such as protein powders or meat-replacers – are highly likely to be carbon-negative, although there are none in the shops today.
Blueberries and celery
Fresh blueberries, which are often packaged in plastic and flown around the world from countries like Peru, making them an extremely high-carbon food. While carbon-negative peatland products exist, they are very rare and hard to identify in the shops at the moment, but this is another space to watch.
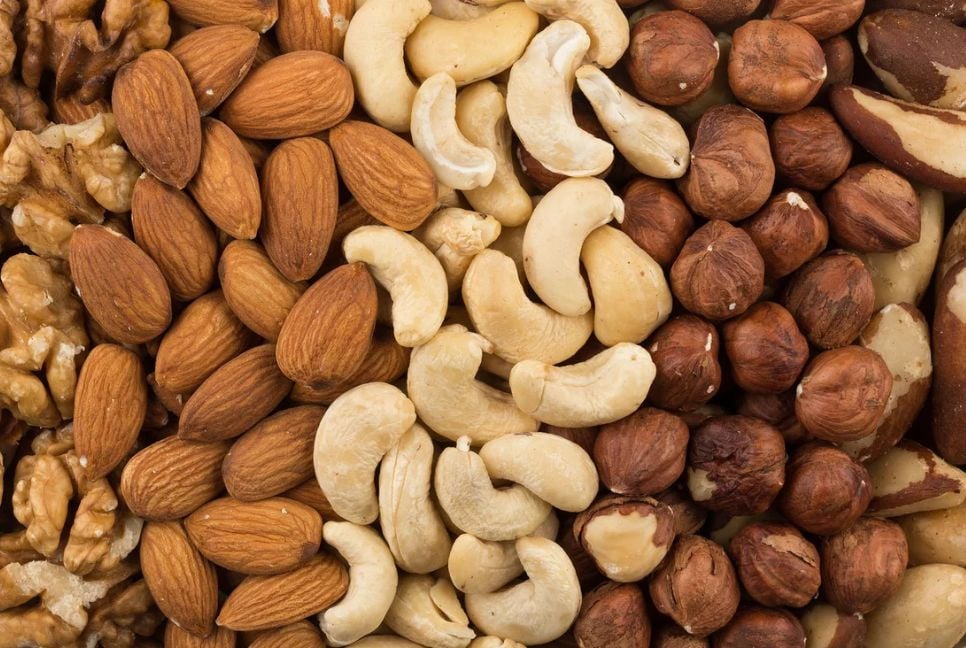
Nuts, olives and citrus
Over the last 20 years, the global area of tree nuts has doubled, and much of this expansion has occurred on croplands. Even accounting for the full supply chain, the typical nut product you will buy in the shops today removes around 1.3kg of CO2 per kg.
These removals last until the trees reach maturity, usually at around 20 years. If the trees are used to make long-lasting wood products at the end of their life, this carbon can remain stored for much longer.
Regeneratively farmed food
Many regenerative practices, such as not tilling the soil or planting hedgerows, can increase the amount of carbon stored in soil or in vegetation. For example, British regenerative farming firm Wildfarmed reports removals of 1.5kg of CO2 for each kg of wheat produced by the growers it works with.
Some companies with carbon-efficient supply chains already say they have turned their products carbon-negative.
However, for high emissions foods, such as beef, research has found that regenerative practices are unlikely to achieve carbon negativity. Further, some regenerative practices can increase emissions elsewhere in the food system.
For example, an Argentinian farm, where the cattle graze at low intensity amongst shrubland, certified its beef as removing 0.3kg of CO2 per kg. To achieve this, it required 500 sq m (5,400 sq ft) of pasture and cropland per kg of beef. If every beef farm used so much land, we would need to convert another three billion hectares (seven billion acres) of land – an area the size of Africa – into farmland to meet our current demand for beef.
Land-sparing foods
For all the potential of carbon-negative foods, they may always only make up a small part of our diets; there just aren't enough products with carbon-negative potential, and regenerative practices probably can't offset high emissions foods. So, we need other strategies for carbon negativity too.
If we stop farming land, it will likely revert back to forest or natural grassland. So if you can produce the same amount of food with less land, the land that is freed up will likely absorb carbon.
One way to spare land is to increase yields: produce more on the same amount of land. However, yield increases tend to be a few percent per year at most, and nowhere near enough to spare enough land to make a product carbon-negative. Something far more powerful is required.
Some products use so much land compared to their alternatives, that swapping away from them can create negative emissions. This is because by sparing land, you are freeing up land for revegetation, which would then absorb carbon from the air.
While carbon labelling and new technologies are vital for our shift to carbon negativity, swapping from products that use lots of land (generally meat and dairy) to products that use little land (generally plant-based foods) is probably the most effective way to make our diets carbon negative.
Source: BBC
Bd-pratidin English/Fariha Nowshin Chinika