The recent sightings of Russell's vipers in rural areas and urban outskirts of Bangladesh have led to increased fear among the public. Widespread rumours have further led to misinformation, misguiding people and causing panic. To address this, it is crucial to evaluate facts about the snake, ensuring communities are better prepared to handle abrupt encounters. Let's go over facts, myths, and the origin of Russell's viper. Source: UNB.
Introducing Russell's Viper
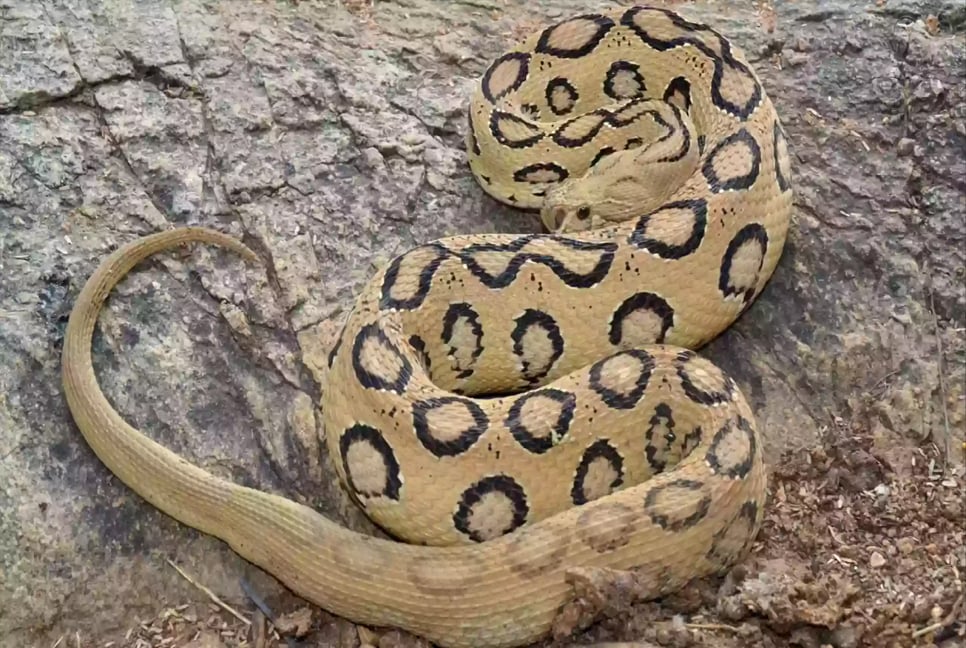
This venomous snake, known scientifically as ‘Daboia russelii’, belongs to the family Viperidae. The species was named in honor of Patrick Russell, a Scottish herpetologist renowned for his pioneering descriptions of many snakes native to India. The genus name, ‘Daboia’, is derived from a Hindi word meaning ‘that lies hid’ or ‘the lurker’.
However, recent studies have reclassified these South Asian snakes as a separate species, ‘Daboia siamensis’. The type locality is specifically listed as Coromandel Coast, India, as inferred by Russell in 1796. This southeastern coastal region of the Indian subcontinent borders the Bay of Bengal, where Bangladesh is also located. In Bangladesh, the snake is known as ‘Chandrabora’.
Originally, this viper was primarily found in the Barendra region of Bangladesh. However, its range has expanded significantly to include areas along the banks of the Padma, Meghna, and Jamuna rivers. The spread of this snake has caused widespread panic in numerous regions, including Barishal, Patuakhali, Manikganj, Faridpur, Shariatpur, Chandpur, and even villages on the outskirts of Dhaka. Presently, this venomous reptile is reported in at least 25 districts across Bangladesh.
Russell's Viper: Myth vs. Reality
False information regarding this viper has been spreading across social media platforms, causing extensive public panic in Bangladesh. These misleading posts have generated significant misconceptions about the snake and its prevalence. However, the facts differ greatly from these rumors. Let's explore the most popular myths and the truths behind them.
Native or Non-native to Bangladesh?
Contrary to popular belief, Russell’s viper is native to Bangladesh as well as other countries in Southeast Asia. It was initially described in 1797 by English naturalist George Shaw and illustrator Frederick Polydore Nodder.
According to the article ‘Russell's Viper (Daboia russelii) in Bangladesh: Its Boom and Threat to Human Life’, of the Asiatic Society of Bangladesh Science in 2018, two species of these snakes exist globally. Daboia Russelii is found in India, Pakistan, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Bhutan, and Bangladesh, whereas Daboia siamensis inhabits China, Thailand, Myanmar, Indonesia, Cambodia, and Taiwan.
The species was classified as 'critically endangered' in 2000 and remained 'near-threatened' at least until 2015 in Bangladesh by the International Union for Conservation of Nature.
Chasing People to Bite?
In 2021, Mongabay published a research paper titled ‘Tracking Russell's viper in rural Karnataka unravels their behavior’, authored by organismal biologist Xavier Glaudas. Throughout his study, Glaudas had numerous close encounters with these vipers, yet remarkably, he was never bitten. He attributed this to the snake's tendency to remain concealed within vegetation. These vipers typically exhibit immobility when approached, occasionally retreating deeper into foliage or retracting their heads for camouflage.
Glaudas emphasized that unprovoked attacks are rare and defined aggressive behavior as defensive biting when startled by human presence. These snakes primarily inhabit grassy lowlands, scrub forests, open woodlands, and agricultural areas, actively avoiding human settlements. Their diet includes rodents, crabs, frogs, lizards, and birds, with no inclination towards human prey.
Contrary to folklore and sensationalized tales, these snakes do not chase humans but are often depicted as aggressive in regional myths and cinema. In reality, they are hesitant to bite, tolerating close proximity and even accidental contact. When sensing danger, they freeze or emit warning hisses as a deterrent. Instances of bites typically occur when individuals inadvertently step on the snake, triggering a defensive reaction.
No Antidote for its Venom?
Fortunately, this is not entirely true as post-venom treatment options are available in Bangladesh. The antivenom is readily available free of charge at all government hospitals across Bangladesh. According to the Venom Research Centre at Chittagong Medical College, these antivenoms are nearly 100 percent effective against the venom. Swift administration of treatment upon being bitten ensures a positive outcome, with fatalities primarily occurring among those who delay seeking medical help.
The government of Bangladesh is taking necessary measures to enhance antivenom distribution, focusing on high-risk regions and ensuring accessibility even in remote areas.
It’s Breath Causes Leprosy?
Similar to other snakes, these vipers produce a hissing sound by exhaling air through their mouth and nose, typically as a warning signal meaning "back off!" This behavior is common among snakes when they feel threatened, angry, or annoyed.
During this hissing display, they often raise about one-third of their front body, signaling a defensive posture. Such bodily raising is a common defensive behavior among snakes, but these vipers are notable for their ability to elevate most of their body off the ground compared to other species.
However, these defensive gestures and sounds do not inflict physical harm on their intended targets beyond intimidation. While their venom is potent and potentially fatal, its effects occur only after a bite, not from mere defensive displays.
Touching It Results in Flesh Rot?
This is also a misconception that lacks scientific basis. Venom is never present on the surface of a snake's body; it is only released when the fangs penetrate a victim's skin during a bite. Even accidentally stepping on a snake with its mouth closed poses no risk of envenomation.
Bottom Line
It is high time to create mass awareness among the general public about the myths surrounding Russell's viper. Panic and a lack of knowledge are the main culprits behind these myths, which have exacerbated the situation even more. Adding to this is the delay in getting immediate treatment after a snakebite, often leading to death. In such emergencies, prompt treatment significantly enhances the likelihood of recovery. Overall, developing a fact-checking attitude without being superstitious is paramount to dealing with any stressful situation.
Bd pratidin English/Lutful Hoque