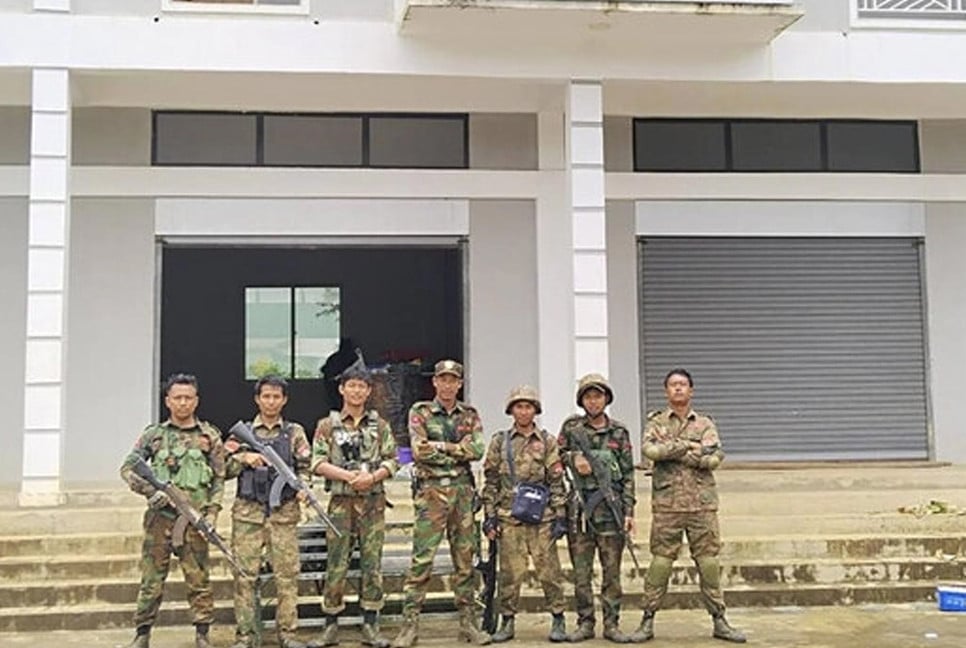
Three well-armed militias launched a surprise joint offensive in northeastern Myanmar a year ago, breaking a strategic stalemate with the regime's military with rapid gains of huge swaths of territory and inspiring others to attack around the country.
The military's control had seemed firmly ensconced with vast superiority in troops and firepower, plus material support from Russia and China. But today the government is increasingly on the back foot, with the loss of dozens of outposts, bases and strategic cities that even its leaders concede would be challenging to take back, reports AP.
“The military is on the defensive all over the country, and every time it puts its energy into one part of the country, it basically has to shift troops and then is vulnerable in other parts,” said Connor Macdonald of the Special Advisory Council for Myanmar advocacy group.
“To us it doesn't look like there's any viable route back for the military to recapture any of the territory that it's lost.”
The military seized power from the elected government of Aung San Suu Kyi in February 2021, triggering intensified fighting with long-established armed militias organized by Myanmar's ethnic minority groups in its border regions, which have struggled for decades for more autonomy.
The army's takeover also sparked the formation of pro-democracy militias known as People's Defense Forces. They support the opposition National Unity Government, which was established by elected lawmakers barred from taking their seats after the army takeover.
But until the launch of Operation 1027, eponymously named for its Oct. 27 start, the military, known as the Tatmadaw, had largely been able to prevent major losses around the country.
Operation 1027 brought coordinated attacks from three of the most powerful ethnic armed groups, known as the Three Brotherhood Alliance: the Myanmar National Democratic Alliance Army, the Arakan Army and the Ta’ang National Liberation Army. The alliance quickly captured towns and overran military bases and outposts along the Chinese border in northeastern Shan state.
Two weeks later, the Arakan Army launched attacks in its western home state of Rakhine, and since then other militia groups and PDFs have joined in around the country.
Myanmar's military has been pushed back to the country's center
A year after the offensive began, resistance forces now fully or partially control a vast horseshoe of territory. It starts in Rakhine state in the west, runs across the north and then heads south into Kayah and Kayin states along the Thai border. The Tatmadaw has pulled back toward central Myanmar, around the capital Naypyidaw and largest city of Yangon.
“I never thought our goals would be achieved so quickly,” Lway Yay Oo, spokesperson for the Ta’ang National Liberation Army, told The Associated Press. “We only thought that we would attack the military council together to the extent we could, but it has been easier than expected so we’ve been able to conquer more quickly.”
Along the way, the Tatmadaw has suffered some humiliating defeats, including the loss of the city of Laukkai in an assault in which the Myanmar National Democratic Alliance Army captured more than 2,000 troops, including six generals; and of the city of Lashio, which had been home to the military's Northeast Command.
“The 1027 offensive was a highly impressive operation, quite complex, and the use of drones played a big role because basically they were able to dismantle the military's network of fire-support bases across northern Shan,” said Morgan Michaels, a Singapore-based analyst with the International Institute of Strategic Studies who runs its Myanmar Conflict Map project.
“And then, once the military's artillery support eroded, they were able to overrun harder targets like towns and battalion headquarters.”
A year later, the military is “substantially weakened,” he said, but it's too early to write it off.
The military has been weakened, but not defeated
The Tatmadaw has managed to claw back the town of Kawlin in the Sagaing region, which had fallen in the first days of the 1027 offensive, stave off an attack by three ethnic Karenni militias on Loikaw, the capital of Kayah state, and has retained administrative control of Myawaddy, a key border crossing with Thailand, after holding off an assault by one ethnic group with the assistance of a rival militia.
Bd-pratidin English/Lutful Hoque